The Continuity Equation in Fluid Mechanics: A Complete Guide
Introduction
The continuity equation is one of the fundamental principles governing fluid flow in civil engineering. Whether you’re designing water distribution systems, analyzing stormwater drainage, or calculating flow in open channels, understanding the continuity equation is essential. This comprehensive guide will walk you through the theory, derivation, and practical applications of this critical concept.
Basic Principles of Fluid Flows
Conservation of Mass
It states that “Matter cannot be created nor destroyed.”
Conservation of Energy
It states that “Energy cannot be created nor destroyed.
Conservation of Momentum
It states that the change in momentum of a body is equal to the product of force and time increment during which it acts.
Conservation of Mass
This principle states that matter cannot be created nor destroyed. In fluid mechanics, this means that the mass of fluid entering a system must equal the mass leaving it (assuming no accumulation). The continuity equation is the direct mathematical expression of this principle applied to flowing fluids.
![]()
Conservation of Energy
Energy cannot be created nor destroyed—it can only change forms. This principle leads to Bernoulli’s equation and the energy equation in fluid mechanics, which we’ll reference when discussing how the continuity equation fits into broader flow analysis.
Conservation of Momentum
This principle states that the change in momentum of a body equals the product of force and time increment during which it acts. While not directly used in deriving the continuity equation, momentum conservation is crucial for analyzing forces in flowing fluids and appears in problems involving jets, pipe bends, and hydraulic structures.
Understanding Flow Rates
Before we proceed to the continuity equation, we need to understand how we quantify fluid flow. There are three primary ways to express flow rate:
Volumetric Flow Rate (Discharge)
Discharge (Q), or commonly known as flow rate, is the volumetric flow rate of liquid which equals to the volume of liquid passing through a given cross-sectional area per unit of time.
Since flow rate/discharge Q represents the volume per unit time, we get:
![]()
![]()
Where:
- Q = volumetric flow rate (m³/s)
- A = cross-sectional area (m²)
- V = average flow velocity (m/s)
What does it mean?: If you imagine water flowing through a pipe, Q tells you how many cubic meters of water pass through any cross-section of that pipe every second.
Mass Flow Rate
Mass flow rate represents the mass of fluid passing through a cross-section per unit time.
![]()
Where:
- ṁ = mass flow rate (kg/s)
- ρ = fluid density (kg/m³)
- Q = volumetric flow rate (m³/s)
- A = cross-sectional area (m²)
- V = average velocity (m/s)
When to use: Mass flow rate is particularly important when dealing with compressible flows (gases) or when temperature changes affect fluid density.
Weight Flow Rate
![]()
Where:
- Ẇ = weight flow rate (N/s)
- γ = specific weight of fluid (N/m³)
- γ = ρ × g (density × gravitational acceleration
What Is Continuity Equation?
At its core, the continuity equation is derived from mass conservation. What goes in (Mass of Fluid Entering) is equal to what goes out (Mass of fluid leaving).
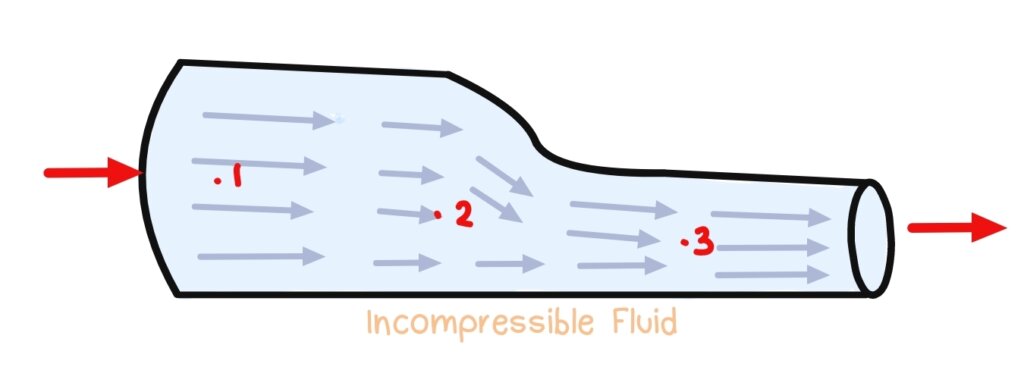
Incompressible flow are common in fluids because the density is constant.
Compressible Flow
Gases
![]()
Incompressible Flow
Common in Fluid
![]()
Where:
A = cross-sectional area (m²)
V = flow velocity (m/s)
References:
Cengel, Y. A., & Cimbala, J. M. (2018). Fluid mechanics: Fundamentals and applications (4th ed.). McGraw-Hill Education.
Munson, B. R., Young, D. F., Okiishi, T. H., & Huebsch, W. W. (2013). Fundamentals of fluid mechanics (7th ed.). John Wiley & Sons.
Streeter, V. L., Wylie, E. B., & Bedford, K. W. (1998). Fluid mechanics (9th ed.). WCB/McGraw-Hill.
White, F. M. (2016). Fluid mechanics (8th ed.). McGraw-Hill Education.
📍This post is part of FLUID MECHANICS COMPLETE Lessons. Also, if you want to avail the complete fluid mechanics formulas just click the image below.