Masonry Works: Estimating CHB, Mortar, and Plaster
Whether you’re a contractor, engineer, or a student, knowing how to estimate Concrete Hollow Blocks (CHB), mortar, and plaster can save time, reduce waste, and control costs.
What is Masonry?
Masonry is the construction of structures using individual units bonded together with mortar. The most common units are:
- Concrete blocks (CHB)
- Clay bricks
- Stones
- AAC blocks (lightweight)
What is CHB?
Concrete Hollow Blocks (CHB) are precast masonry units widely used in residential and commercial construction.
Estimating Concrete Hollow Blocks
CONCRETE HOLLOW BLOCKS
Step 1: Determine the Wall Area
![]()
A wall is 10 meters long and 3 meters high.
![]()
Step 2: Calculate the Total Wall Area
![]()
There’s a door of 0.9 x 2.1 m and a window of 0.6 x 0.7, subtract:
![]()
Step 4: Multiply by 12.5
![]()
![]()
Estimating Cement Mortar
CEMENT MORTAR BASED ON CHB PCS
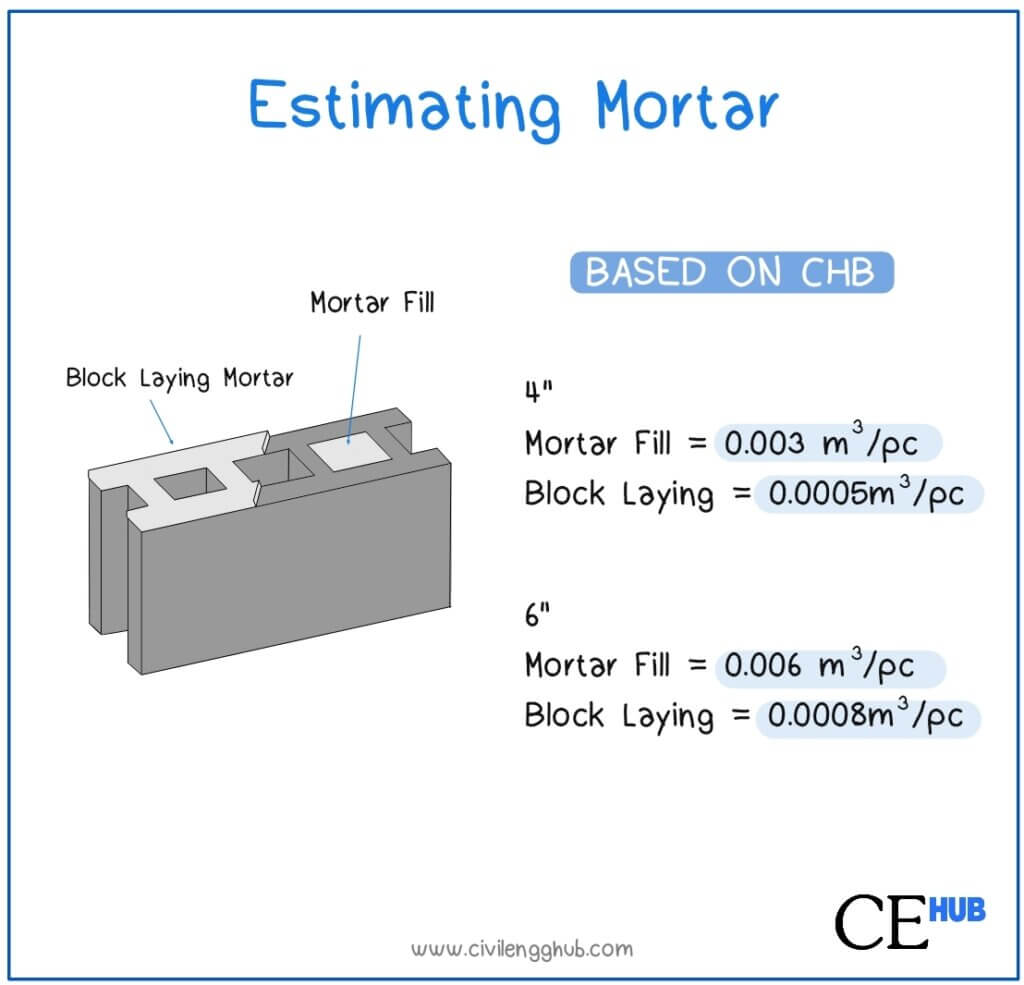
For 4″
| Mortar Fill | 0.003 m^3/pc |
| Block Laying Mortar | 0.0005 m^3/pc |
For 6″
| Mortar Fill | 0.006 m^3/pc |
| Block Laying Mortar | 0.0008 m^3/pc |
Step 1: Multiply the CHB pcs to the multipliers.
Get the number of CHB from above, 347 pcs.
![]()
![]()
Step 2: Add mortar fill + block laying mortar
![]()
Step 3: Identify Class and kg of bags, then multiply
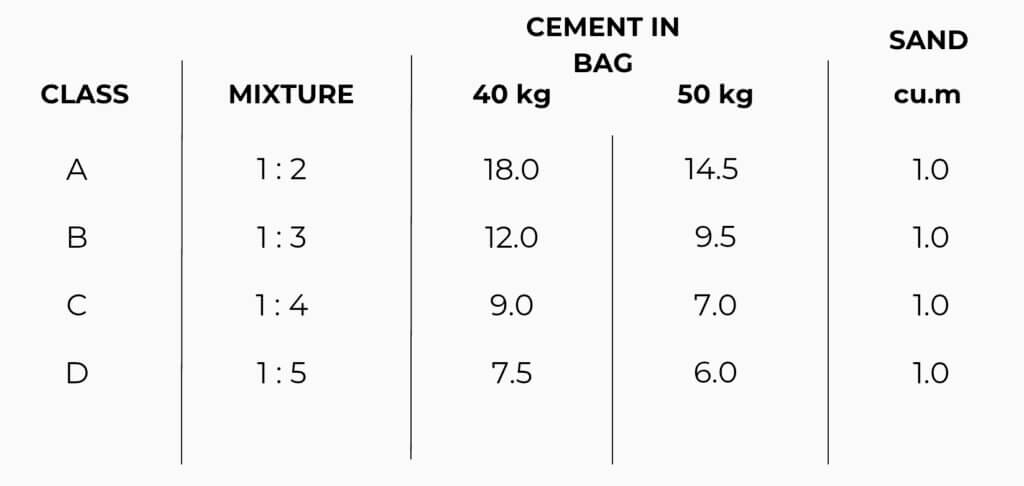
Use class B & 40 kg,
CEMENT MORTAR BASED ON SQ. M
Step 1: Get the Net Area
From what we get before, it’s
Step 2: Multiply to the multiplier:
For 4″
| Mortar (combined fill and block laying) | 0.0438 m |
For 6″
| Mortar (combined fill and block laying) | 0.0844 m |
if we look at the value, it’s almost the same with the value with the chb method.
Step 3: Identify Class and kg of bags, then multiply

Use class B & 40 kg,
Estimating Plaster
PLASTER (VOLUME METHOD)
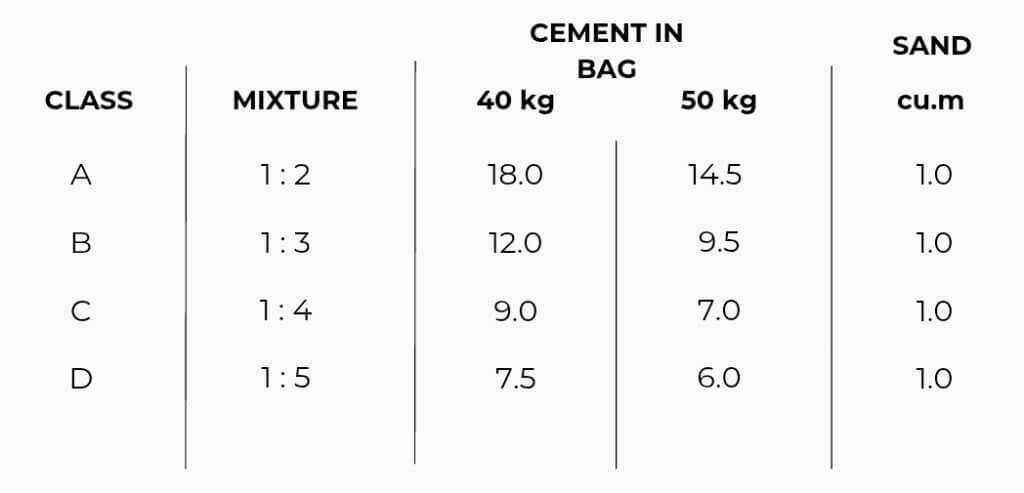
Using 40 kg, Class B
Example
PLASTER (AREA METHOD)
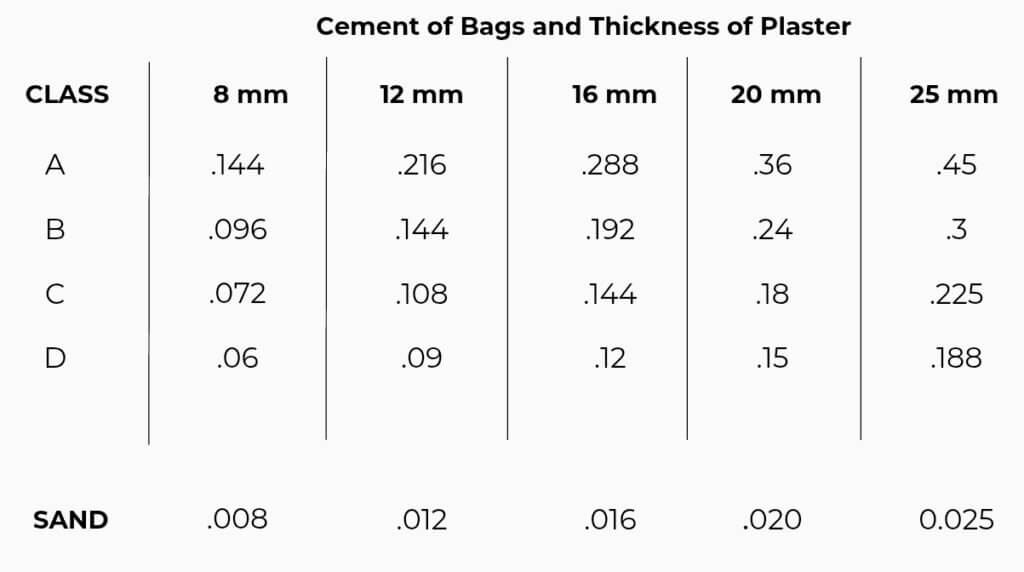
Using 40 kg, Class B
References:
Fajardo, M. B. (1980). Simplified Construction Estimate.