Metal reinforcements in Construction and Estimate plays a crucial role in construction projects, ensuring that the correct amount of steel reinforcement is used while optimizing costs.
What is Steel?
Steel is the most widely used reinforcing material in the construction world. While concrete is strong in compression, it is weak in tension. This is where steel plays a crucial role, as it excels in resisting tensile forces. Combining these two makes a good structural combination that is capable of withstanding compressive and tensile stresses.
Vertical and Horizontal Reinforcements
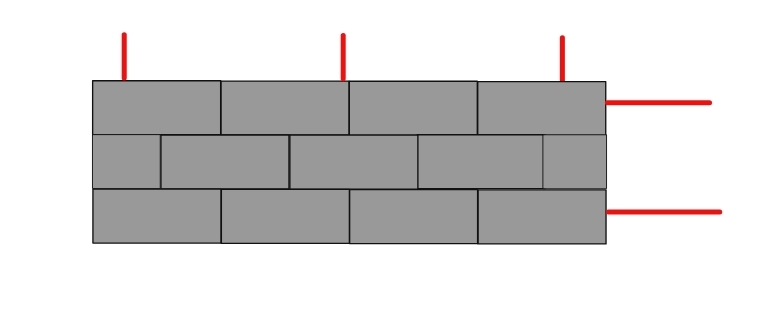
Example: You are assigned to design a CHB wall for a fence. The wall is 5 meters high and 25 meters long. The CHB units are standard size. Vertical steel reinforcements are placed every 40 cm, and horizontal reinforcements are placed every 3 layers of CHB.
Step 1: Determine the Area
\[ A = L \times \]
$ A = 25 \times 5 $
Step 2: Check the requirement for horizontal reinforcements (layers) and vertical reinforcements (spacing).
Vertical bars every 40 cm, and Horizontal Bars every 3 layers. We got 2.93
Step 3: Multiply the Area to the multiplier
Vertical Reinforcements:
Horizontal Reinforcements:
Step 4: Add the vertical and horizontal reinforcements.
Step 5: Find the appropriate length of steel bars commercially available.
You can choose from 6, 7.5, 9, 10.5 and 12 m, depending on your project. In this case, I chose 6 meters.
Order 106 pcs of 6 m.
Tie Wire
Step 1: Refer to the table.
Tie wires can range from 25 cm to 40 cm, up to you as a quantity surveyor. In this problem, I’ll use 30 cm. In our problem, we used vertical bars every 40 cm and horizontal bars every 3 layers. So our coefficient will be 0.047.
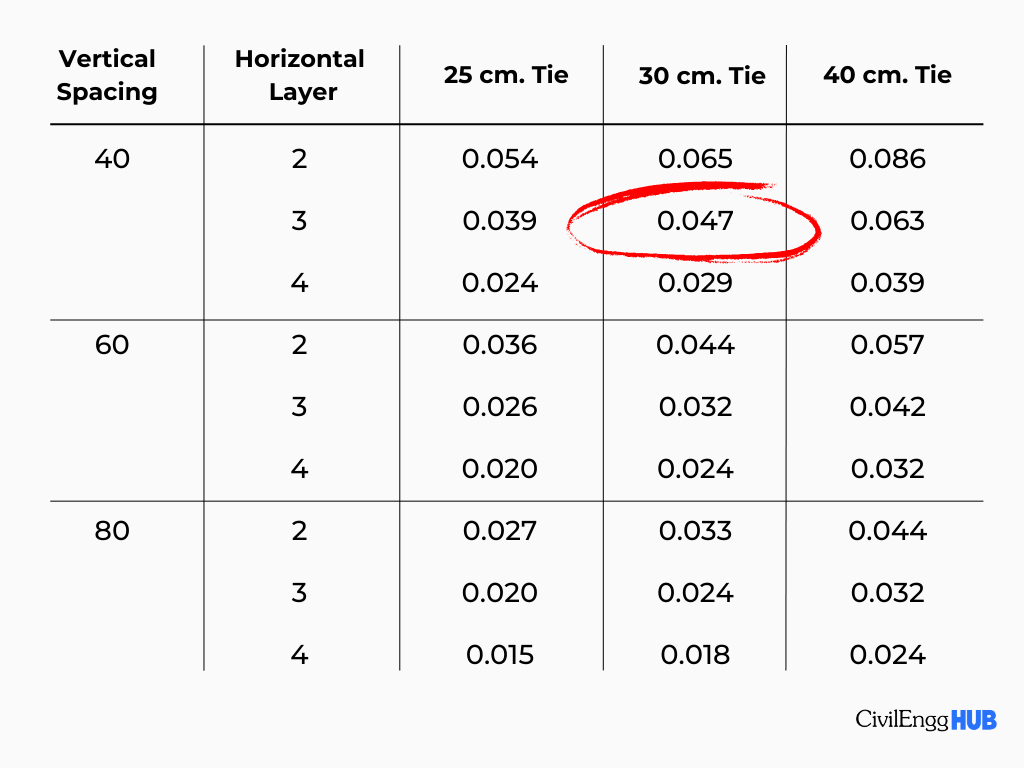
Step 2: Multiply area by the coefficient.
Tie Wire
Using the problem before.
1. Find the area of the wall.
2. Refer to the table and check the conditions.
Tie wires can range from 25 cm to 40 cm, up to you as a quantity surveyor. In this problem, I’ll use 30 cm. In our problem, we used vertical bars every 40 cm and horizontal bars every 3 layers. So our coefficient will be 0.047.
3. Multiply area by the coefficient
Footing Metal Reinforcement
Example: You are designing a 2-story building with 16 isolated square footings in the plan. The footing has a dimension of 1 meter x 1 meter and a thickness of 0.3 meters. The protective cover is 75mm. Bar spacing is 135 mm both directions.
1. Find the Length, Width, and protective cover of the footing
2. Length minus protective cover

3. Choose from a commercial-length steel bar
- 6 m
- 7.5 m
- 9 m
- 10.5 m
- 12 m
When choosing between the length of steel bars, it is important to determine the excess, also known as waste.
for example:
6m:
7.5 m:
9m:
In 6 m, we can cut 7 times because we only accept the whole number; therefore, there’s only 0.059 excess, while in 7.5 m and 9 m lengths, there will be a lot of waste; therefore, it is economical to use 6m in this problem.
4. Determine the bar spacing or use the direct counting method.
The direct counting method is counting the number of bars directly from the plan. But in our case, it is not specified; rather, the bar spacing is given as 135mm:
5. Find the total number of bars in all the footings
6. Divide the total number of bars by the number of cuts
order
Tie Wires
Note: Tie wire can range from 0.2m to 0.4m per intersection.

For the example above, we have 8×8 intersections and 16 footings.
order
References:
Fajardo, M. B. (1980). Simplified Construction Estimate.
HOW TO: Calculate Steel Reinforcement Quantity for Concrete Footing Foundation. (2025). Veriaconcyclopedia.com. https://www.veriaconcyclopedia.com/v/esti/esti-cfr