Principles of Fluid flow, Discharge and Continuity Equation
What you’ll learn
Basic Principles of Fluid Flows
Conservation of Mass
It states that “Matter cannot be created nor destroyed.”
Conservation of Energy
It states that “Energy cannot be created nor destroyed.
Conservation of Momentum
It states that the change in momentum of a body is equal to the product of force and time increment during which it acts.
What is Discharge?
Discharge (Q), or commonly known as flow rate, is the volumetric flow rate of liquid which equals to the volume of liquid passing through a given cross-sectional area per unit of time.
Mass Flow Rate
Volume Flow Rate
Since flow rate Q represents the volume per unit time, we get:
Weight Flow Rate
What Is Continuity Equation?
At its core, the continuity equation is derived from mass conservation. What goes in (Mass of Fluid Entering) is equal to what goes out (Mass of fluid leaving).
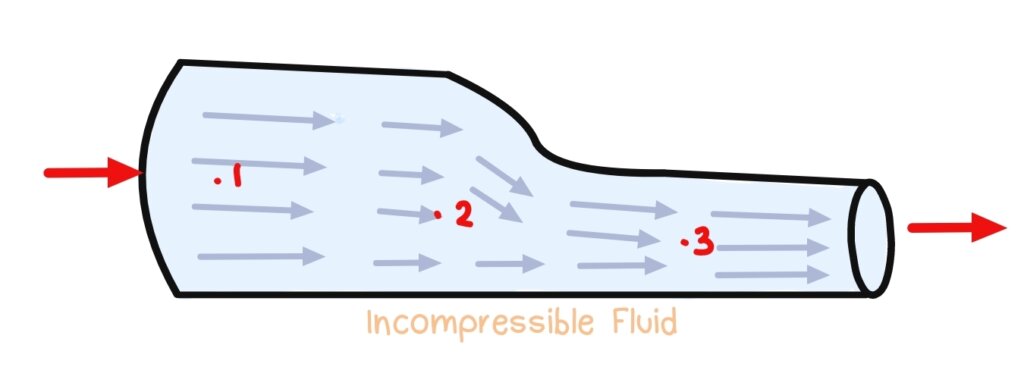
Incompressible flow are common in fluids because the density is constant.
Compressible Flow
Gases
Incompressible Flow
Common in Fluid
Where:
A = cross-sectional area (m²)
V = flow velocity (m/s)