What you’ll learn
- Concept of Seismic Base Shear
- Computing base shear
- Determining the vertical distribution of lateral loads acting on each story
Seismic base shear, despite its technical air, plays a vital role in earthquake-resistant design—a concept as often mischaracterized as it is crucial. Rather than a figure arbitrarily derived from a formula, base shear refers to the lateral force that a building’s foundation must withstand when subjected to earthquake ground motions. Understanding this force isn’t merely academic; it’s indispensable for structural safety and the integrity of earthquake-prone buildings. Ignoring the importance of base shear in design would significantly compromise a structure’s performance during seismic events.
Seismic Base Shear
If you imagine the ground beneath a building suddenly shifting, yet the building itself naturally wants to resist that movement because of inertia. This dynamic produces lateral forces across the base. The sum of these horizontal forces at the bottom of the structure is defined as the base shear—an important factor in structural engineering, as it influences how buildings are designed to withstand earthquakes.
Structure Period
Ct = 0.0853 for steel moment resisting frames
Ct = 0.0731 for concrete moment resisting frames
Ct = 0.0488 for all other buildings
Design Base Shear
The total design base shear shall not exceed:
The total design base shear shall not be less than:
Vertical Distribution Force
EXAMPLE 1.0
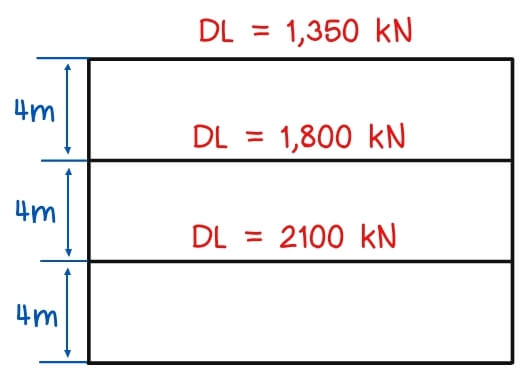
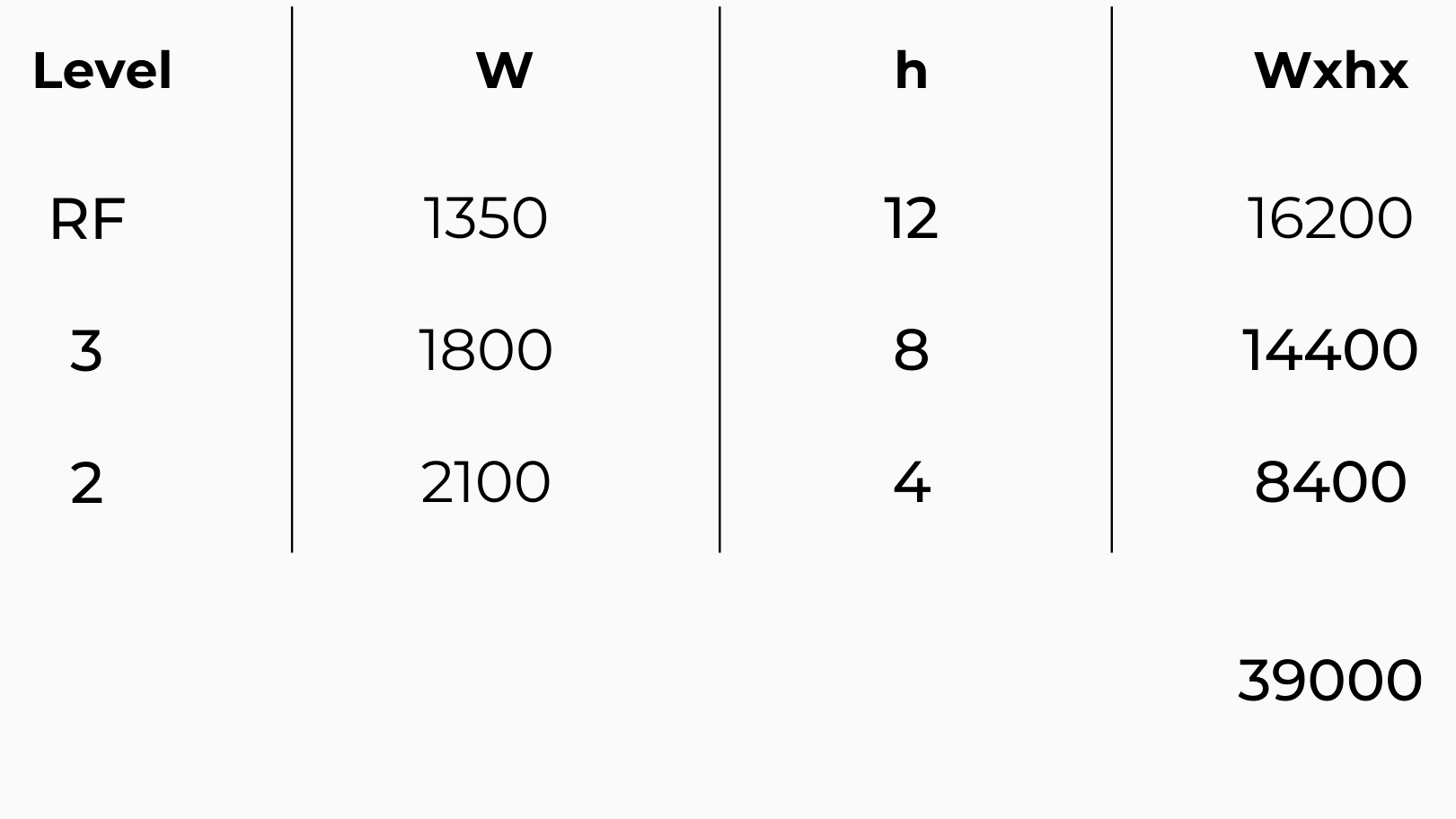
1. A three-story building with a special moment-resisting steel frame has a calculated base shear of 450,000 N. The tributary dead loads of each story, including walls, are given in the following.
a) What is the lateral force at the roof of the building?


EXAMPLE 2.0
2. A proposed 8-story, 10 x 20-meter hospital is to be constructed with reinforced concrete with special moment-resisting frames. Assume the regular weight per floor area to be 10 kPa, while the roof deck weighs 6 kPa. Each floor has a height of 3 m, except the first floor, which is 3.4 m. Assume seismic source type A. Nv = 1.6, Na = 1.2
a) Calculate the story forces and story shears.
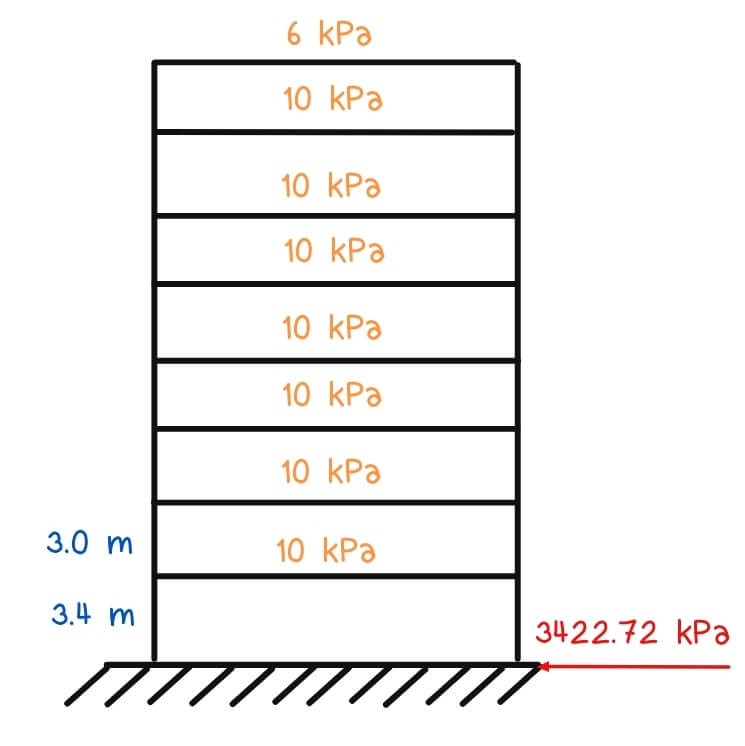






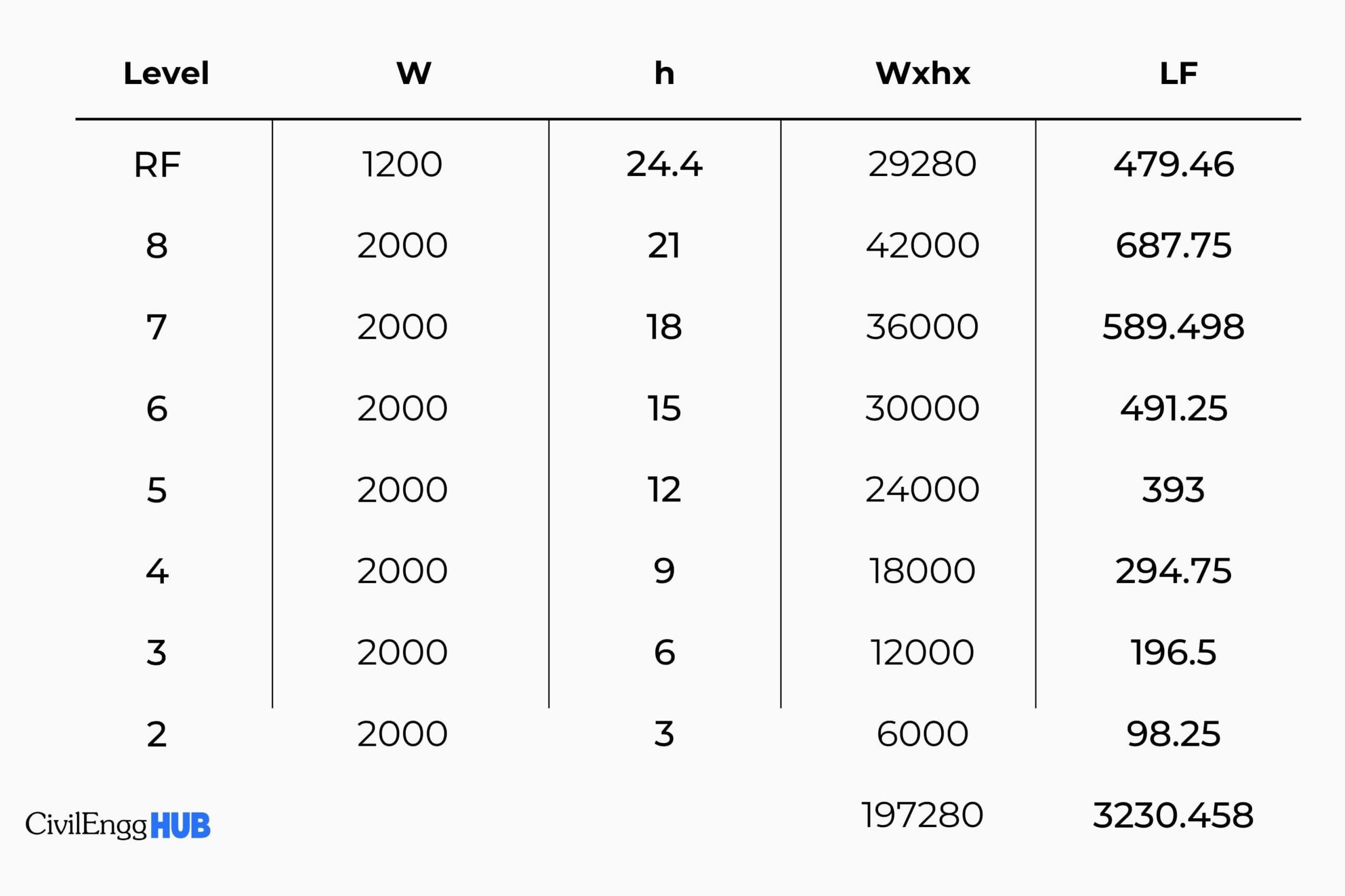
input the values for others as well:
EXAMPLE 3.0
3. A ten-story office building with a special moment-resisting steel frame, has a height per each floor of 3.5 m and a weight for each story of 60500 kg . Determine the base shear.
Other information:
Seismic Zone 4
Near source factor, Nv=1.0


EXAMPLE 4.0
4. A four-story residential reinforced concrete building has a structural system of special-moment resisting frame system (SMRF), has a height per each floor of 3m except GF=4.0 m. The building dimension is 5m x 10 m, and a weight per floor of 8 kPa.
Other information:
Soil Profile, unknown
Distance to nearest fault line = 5 km
Determine the Period, T and the Base Shear, V.

Base Shear